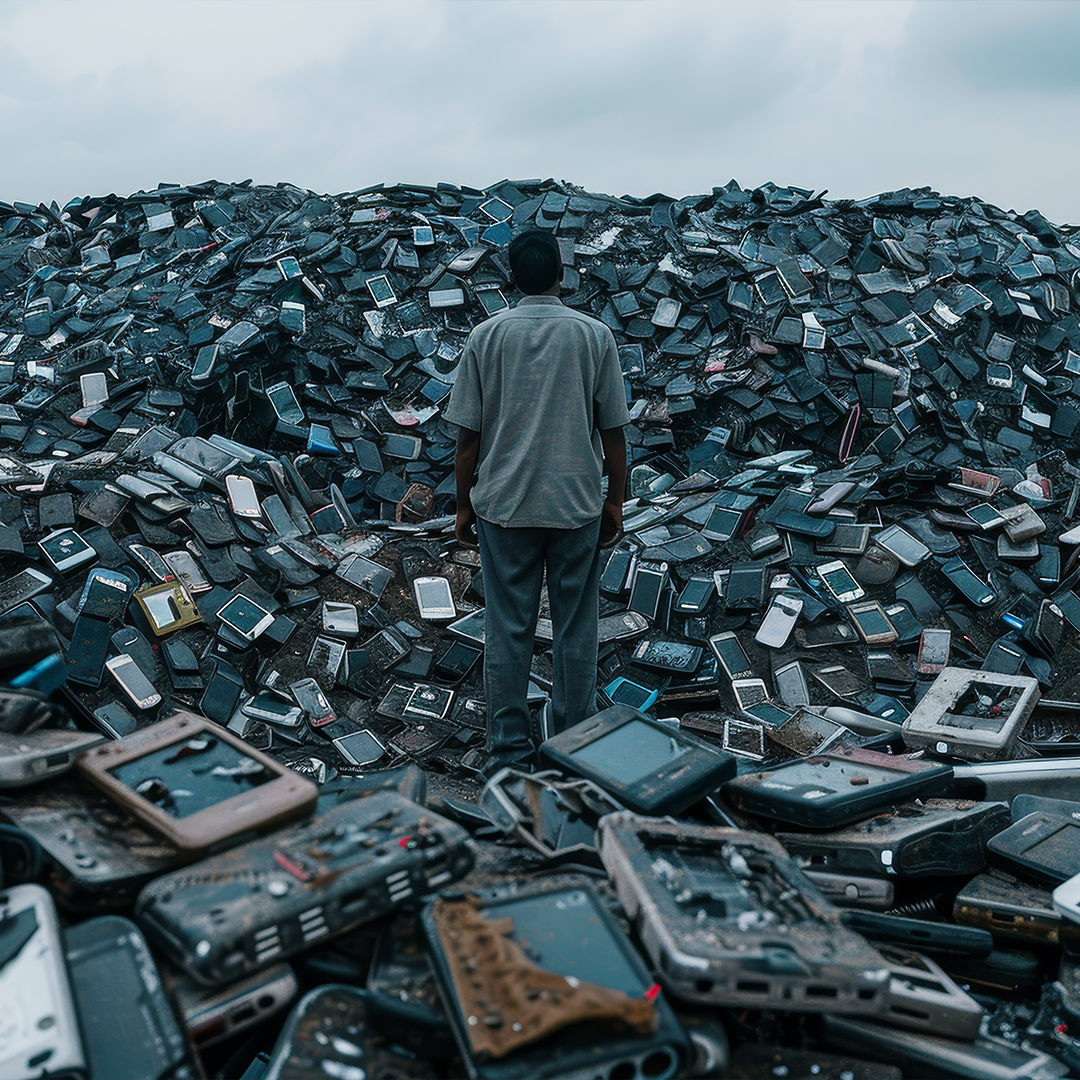
In the digital age, electronic devices have become an essential part of our daily lives. From smartphones and computers to household appliances and batteries, technology is advancing at a rapid pace. However, the constant replacement and disposal of these products creates a massive environmental problem: electronic waste, also known as e-waste.
In the digital age, electronic devices have become an essential part of our daily lives. From smartphones and computers to household appliances and batteries, technology is advancing at a rapid pace. However, the constant replacement and disposal of these products creates a massive environmental problem: electronic waste, also known as e-waste.
The Exponential Growth of Electronic Waste
Every year, millions of tons of electronic waste are generated worldwide. According to recent studies, the amount of e-waste has increased considerably due to the increasingly short life cycle of devices and the planned obsolescence imposed by many technology companies. This situation poses an enormous challenge for the proper management and treatment of this waste.
Environmental Impact and Health Risks
E-waste contains toxic materials such as lead, mercury, cadmium, and brominated flame retardants, which can leach into the soil and waterways if not disposed of properly. These pollutants affect not only the environment but also human health, causing respiratory illnesses, neurological damage, and immune system problems.
Furthermore, the extraction of precious metals such as gold and copper in electronic devices has devastating impacts on natural ecosystems, leading to deforestation and water pollution.
Sustainable Solutions and Alternatives
To mitigate the impact of e-waste, it is essential to adopt recycling and reuse practices. Some solutions include:
Conclusion
The problem of e-waste is a silent crisis that requires urgent attention. As consumers, we have a responsibility to be aware of the environmental impact of our technology and take steps to reduce our electronic footprint. Through education, recycling, and more responsible consumption, we can contribute to environmental preservation and protect the health of future generations.